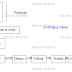
SPIRAL MODEL
Ø The Spiral Model is similar to the incremental model, with more
emphasis placed on risk analysis.
Ø In spiral Model, the angular component represents “PROGRESS” &
the radial component represent “COST”.
Ø Each cycle in the spiral begins with the identification of
objectives for that cycle, the different alternatives that r possible for
achieving the objectives & the constraint that exist.
Ø Next Step in the cycle is to evaluate these different alternatives
based on objectives & constraint, design for that cycle. The focus of evaluation in this step is
based on the risk perception for the project. Risk reflects the chances
that some of the objectives of the project may be not met.
Ø The next step is to develop strategies that resolve uncertainties
& risk. This step may involve activities such as benchmarking, simulation
& prototyping.
Ø Finally in 4th quadrant we plan for the next cycle or
module.
Ø The spiral model works for development as well as enhancement
projects.
ADVANTAGES
1)
High amt of risk analysis, so
preferred for high risks projects.
2)
Good for large & mission
critical projects.
3)
S/W is produced early in the
s/w life cycle.
DISADVANTAGES
1)
Can be a costly model to use.
2)
Risk analysis requires specific
expertise...
3)
Project’s success is highly
dependent.







0 comments: