Friday, March 22, 2013
Thursday, March 21, 2013
V-Model
by Gaurav Sharma |
in Tutorial
at 6:55 AM
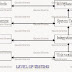
V-MODEL
Ø Just
like the WFM, the V-shaped life cycle is a sequential path of execution of
process
Ø Each
phase must be completed before the next phase begins.
Ø Testing
is emphasized in this model more.
Ø The
testing procedures are developed early in the life cycle before any coding is
done, during each of the phases preceding implementation.
Ø Requirements
begin the life cycle just like the WFM. Before development is started, a system
test plan is created. The test plan focuses on meeting the functionality
specified in the requirements gathering.
Ø The
design phase focuses on system architecture & design. An integration test
plan is created in this phase as well in order to test the piece of s/w systems
ability to work together.
Ø The
low Level Design (Coding) phase is where the actual s/w component are designed
& unit tests are created in this phase as well.
Ø Once
Coding is completed, the path of execution continues up the right side of the
V, where the test plans developed earlier are now put to use.
ADVANTAGES
1) Simple
& easy to use.
2) Each
phase has specific deliverables.
3) Higher
chance of success over the WFM due to the development of test plans early on
during the life cycle.
4) Works
well for small projects where requirements r easily understood.
DISADVANTAGES
1)
Very rigid, like WFM(It needs lot of resources &
money)
2)
S/W is developed during the implementation phase, so no
early prototype of the s/w is produced.
3)
Model doesn’t provide a clear path problem found during
testing phase.
4)
Little flexible & adjusting scope is difficult
& expensive.
Wednesday, March 20, 2013
Spiral Model
by Gaurav Sharma |
in Tutorial
at 4:37 AM
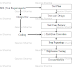
SPIRAL MODEL
Ø The Spiral Model is similar to the incremental model, with more
emphasis placed on risk analysis.
Ø In spiral Model, the angular component represents “PROGRESS” &
the radial component represent “COST”.
Ø Each cycle in the spiral begins with the identification of
objectives for that cycle, the different alternatives that r possible for
achieving the objectives & the constraint that exist.
Ø Next Step in the cycle is to evaluate these different alternatives
based on objectives & constraint, design for that cycle. The focus of evaluation in this step is
based on the risk perception for the project. Risk reflects the chances
that some of the objectives of the project may be not met.
Ø The next step is to develop strategies that resolve uncertainties
& risk. This step may involve activities such as benchmarking, simulation
& prototyping.
Ø Finally in 4th quadrant we plan for the next cycle or
module.
Ø The spiral model works for development as well as enhancement
projects.
ADVANTAGES
1)
High amt of risk analysis, so
preferred for high risks projects.
2)
Good for large & mission
critical projects.
3)
S/W is produced early in the
s/w life cycle.
DISADVANTAGES
1)
Can be a costly model to use.
2)
Risk analysis requires specific
expertise...
3)
Project’s success is highly
dependent.
Monday, March 18, 2013
Evolutionary Model
by Gaurav Sharma |
in Tutorial
at 11:42 PM
ITERATIVE ENHANCEMENT or EVOLUTIONARY MODEL
Ø This model counters the limitation of WFM that requirements be
completely specified before the rest of the development can proceed & tries
to combine the benefits of both prototyping & WFM.
Ø One effective use of this type of model is for product development.
Ø The s/w should be developed in increments, each increment adding
some functional capability to the system until the full system is implemented.
Ø At each step (iteration), extensions & design modification can
be made.
Ø Each iteration passes through the requirements, design,
implementation & testing process.
Ø A working version of s/w is produced during the first iteration, so
u have working s/w early on during the s/w development life cycle.
Ø Subsequent iterations build on the initial s/w produced during the
first iteration.
Ø First a version is released that contains some capability. Based on
feedback from users & experience with this version, a list of additional desirable’s
features & capabilities is generated. These features form the basis of
enhancement of the s/w & are included in the next version.
The first
version contains some core capabilities & then more are added to later
versions.
ADVANTAGES
1)
Generates working s/w quickly
& early during the s/w life cycle.
2)
More flexible –less costly to
change scope & requirements.
3)
Easier to test & debug in
each increments than testing entire system as in WFM.
4)
Easier to manage risk becoz
risky pieces r identified & handled during its iterations.
5)
Each iteration is an easily
managed milestone.
DISADVANTAGES
1)
In generating business
contract- how will the cost of additional features be determined &
negotiated, particularly becoz the client organization is likely to be tied to
the original vendor who developed the first version.
2)
Problems may arise pertaining
to system architecture becoz not all requirements are gathered up front for the
entire s/w life cycle.
3)
Each phase of an iteration is
rigid & do not overlap each other.
Sunday, March 17, 2013
Prototyping Model
by Gaurav Sharma |
in Tutorial
at 11:10 PM
PROTOTYPING MODEL
Ø The goal of a prototyping –based development process is to counter
the limitation of WFM. Requirement frozen.
Ø Instead of freezing the requirements before any design or coding can proceed, a throwaway prototype
is built to help understand the requirements. This prototype is developed based
on the currently known requirements.
Ø By using this prototype, the client can get an actual feel of the
system, because the intraction with the prototype can enable the client to
better understand the requirements of the desired system. This results in more
stable requirements that change less frequently.
Ø After the prototype has been developed, the end user & clients
are given an opportunity to use the prototype & play with it.
Ø Based on their experience, they provide feedback to the developers
regarding the prototype: What is correct, what needs to be modified, what is
missing, what is not needed.
Ø Based on the feedback, the initial requirements are modified to
produce the final requirements specification, which is then used to develop the
production quality system.
ADVANTAGES
1)
It is well suited for projects
where requirements are hard to determine & the confidence in obtained
requirements is low.
2)
It is an excellent technique
for reducing some types of risks associated with a project.
3)
By using COST CUTTING METHODS,
it is possible to keep the cost of prototype less than a few percent of the
total development cost. COST CUTTING METHODS-Minimal documentation,
Reduce Testing.
DISADVANTAGES
1)
Inferior, temporary design
solutions may become permanent
after a while, when the developers has forgotten that they were only intended to be
temporary.(Result in poor software quality)
2)
Customer may object to
prototyping being thrown away & may
demand “ a few changes” to make it working .(Result in poor s/w quality &
maintainability)
3)
MINIMAL DOCUMENTATION may cause
problem, in prototyping. Design doc, a test plan, a test case specification r
not needed during the development of prototype. REDUCE TESTING
cost cutting measures-but results in low quality product.
èPrototyping is often not used , as
it is feared that development costs may become large. However, in some
situations, the cost of s/w development without prototyping may be more than
with prototyping. There r two major reason for that………..
a)
The experience of developing
the prototyping might reduce the cost of the the later phases when the actual
software development is done.
b)
In many projects the
requirements are constantly changing, particularly when development takes a
long time.
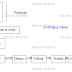
Waterfall Model
by Gaurav Sharma |
in Tutorial
at 9:42 AM
WATERFALL MODEL
Ø WFM
states that the phases are organized in a linear order. It is also referred as
linear sequential life cycle model.
Ø Each
phase must be completed in its entirety, before the next phase can begin.
Ø There
r 2 assumptions made, when we work with WFM
v For
a successful project resulting in a successful product, all phases listed in
WFM must be performed in anyways.
v Any
different ordering of the phases will result in a less successful software
product.
Ø In
a typical model, a project begins with feasibility study. On successful
demonstrating the feasibility of project, the requirements analysis &
project planning begins. The design Starts after the requirements analysis is
completed & coding begin after the design is completed. Once the
programming is completed, the code is integrated & testing is done. On
successful completion of testing, the system is installed. After this, the
regular operations & maintenance of the system takes place.
Ø When
the activities of the phase r completed, there should be some product that is
produced by the phase. The Goal of a phase is to produce this product. The o/ps
of the earlier phases r often called WORK PRODUCTs (or intermediate products)
& r usually in the form of documents like the requirement doc or design
doc.
Ø O/Ps
of phases r-
1>Requirement Doc
2>Project Plan
3>System Design Doc
4>Detailed Design Doc
5>Test plan & Test Reports
6>Final Code
7>Software manual(e.g. User, installation etc)
1>Requirement Doc
2>Project Plan
3>System Design Doc
4>Detailed Design Doc
5>Test plan & Test Reports
6>Final Code
7>Software manual(e.g. User, installation etc)
ADVANTAGES
1) Simple
& easy to use.
2) Phases
r processed & completed one at a time.
3) Work
well for smaller projects where requirements are very well understood.
4) Easy
to manage due to rigidity of Model-each phase has specific deliverables & a
review process.
DISADVANTAGES
1) The
requirements of the system can be frozen before the design begin, we can’t
change SRS if design is done.
2) Working
s/w produced at the end of all phases so there is a long wait.
3) High
amt of risk & uncertainty.
4) Poor
Model where requirements r at a moderate –high risk of changing.
5) Poor
Model for long n ongoing projects.
6) Poor
Model for complex & Object oriented projects.
Proudly Powered by Blogger.